
The Gift of the Magi
key terms
cell - smallest functional unit of an organism
tissue - material composed of specialized cells and products
organ - collection of tissues with a specific function
system - roots or shoots
plant tissues
dermal tissue - (epidermis) - outer, protective cell layer equivalent to skin
vascular tissue - conducts material throughout the plant equivalent to circular or resp.
ground tissue - any other tissue that is not dermal or vascular
meristematic tissue (meristems) - able to divide and grow
epidermis
outer layer of cells on plant (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, seeds)
cuticle - waxy layer covering the epidermis that shows water loss from the plant
vascular tissue
xylem - transports water and minerals up from the roots (only ever moves stuff up)
dead tissue, acts like a straw
phloem - moves sugars, other compounds throughout plant (can move stuff in any direction)
ground tissue
parenchyma - thin cell walls and very flexible functions
collenchyma - slightly thickened cell walls for structure
sclerenchyma - very thick cell walls fortified with lignin (chief component of wood) for strength
meristematic tissue
apical meristem - tip of a root or shoot for length or height
intercalary meristem - add height in grasses specifically
axillary meristem - produce branches on roots or shoots
secondary meristem - increase width (cambium)
morphology and anatomy
morphology - external form and structure - as visible from the OUTSIDE
anatomy - internal structure - as visible from the INSIDE
roots
root function
anchor plant in soil
support upright growth
absorb minerals
store energy reserves
anchor
anchor - plants are sedentary (unable to move)
support
support - good root health is essential to grow strong, tall roots
lodging - plants fall over
root lodging - root damage or improper development
absorb
water and dissolved nutrients enter the root vascular tissue
root hairs are responsible for a majority of plant water and nutrient uptake
storage
roots can be used to store energy needed by the plant later in its life
roots also use energy because they are actively growing (meristems)
root morphology
taproot - obvious ain root with smaller branches
fibrous root - lots of smaller roots with many branches
adventitious roots - grow from odd places on stems, leaves etc
ex. corn brace/prop roots
ex. white clover
monocots - fibrous root system
dicots - taproot system
root anatomy
what do roots look like from the inside?
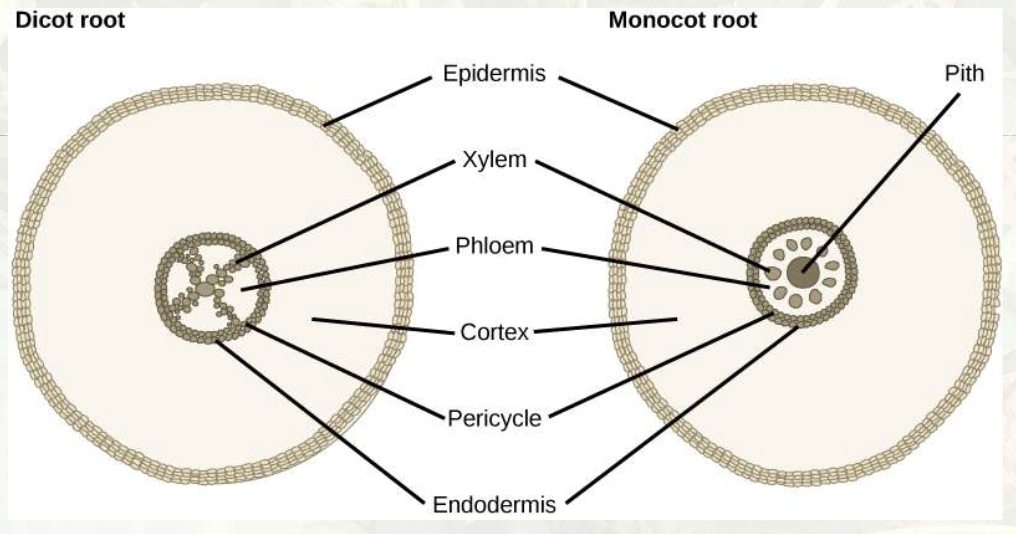
dicot root
epidermis - outer cells taht protect the root(dermal tissue)
cortex - bulk of root structure usually ground tissue ised for storage
endodermis - surrounds vascular tissue in center
pericycle - meristematic tissue along endodermis (source of lateral root)
casparian strip - waxy layer that controls ewater movemet
phloem - living tissye that transports sugars and other compounds
xylem - deas tissye taht acts like a straw and moves water and nutrients up from roots
vascular cambium - meristematic tissue to make new cells
stele - central region containing vascular tissue and pericycle
monocot root
epidermis
cortex
endodermis
pericycle
casparian strip
phloem
vascular cambium
meristematic tissue
pith - central core of ground cells
key terms
cell - smallest functional unit of an organism
tissue - material composed of specialized cells and products
organ - collection of tissues with a specific function
system - roots or shoots
plant tissues
dermal tissue - (epidermis) - outer, protective cell layer equivalent to skin
vascular tissue - conducts material throughout the plant equivalent to circular or resp.
ground tissue - any other tissue that is not dermal or vascular
meristematic tissue (meristems) - able to divide and grow
epidermis
outer layer of cells on plant (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, seeds)
cuticle - waxy layer covering the epidermis that shows water loss from the plant
vascular tissue
xylem - transports water and minerals up from the roots (only ever moves stuff up)
dead tissue, acts like a straw
phloem - moves sugars, other compounds throughout plant (can move stuff in any direction)
ground tissue
parenchyma - thin cell walls and very flexible functions
collenchyma - slightly thickened cell walls for structure
sclerenchyma - very thick cell walls fortified with lignin (chief component of wood) for strength
meristematic tissue
apical meristem - tip of a root or shoot for length or height
intercalary meristem - add height in grasses specifically
axillary meristem - produce branches on roots or shoots
secondary meristem - increase width (cambium)
morphology and anatomy
morphology - external form and structure - as visible from the OUTSIDE
anatomy - internal structure - as visible from the INSIDE
roots
root function
anchor plant in soil
support upright growth
absorb minerals
store energy reserves
anchor
anchor - plants are sedentary (unable to move)
support
support - good root health is essential to grow strong, tall roots
lodging - plants fall over
root lodging - root damage or improper development
absorb
water and dissolved nutrients enter the root vascular tissue
root hairs are responsible for a majority of plant water and nutrient uptake
storage
roots can be used to store energy needed by the plant later in its life
roots also use energy because they are actively growing (meristems)
root morphology
taproot - obvious ain root with smaller branches
fibrous root - lots of smaller roots with many branches
adventitious roots - grow from odd places on stems, leaves etc
ex. corn brace/prop roots
ex. white clover
monocots - fibrous root system
dicots - taproot system
root anatomy
what do roots look like from the inside?

dicot root
epidermis - outer cells taht protect the root(dermal tissue)
cortex - bulk of root structure usually ground tissue ised for storage
endodermis - surrounds vascular tissue in center
pericycle - meristematic tissue along endodermis (source of lateral root)
casparian strip - waxy layer that controls ewater movemet
phloem - living tissye that transports sugars and other compounds
xylem - deas tissye taht acts like a straw and moves water and nutrients up from roots
vascular cambium - meristematic tissue to make new cells
stele - central region containing vascular tissue and pericycle
monocot root
epidermis
cortex
endodermis
pericycle
casparian strip
phloem
vascular cambium
meristematic tissue
pith - central core of ground cells